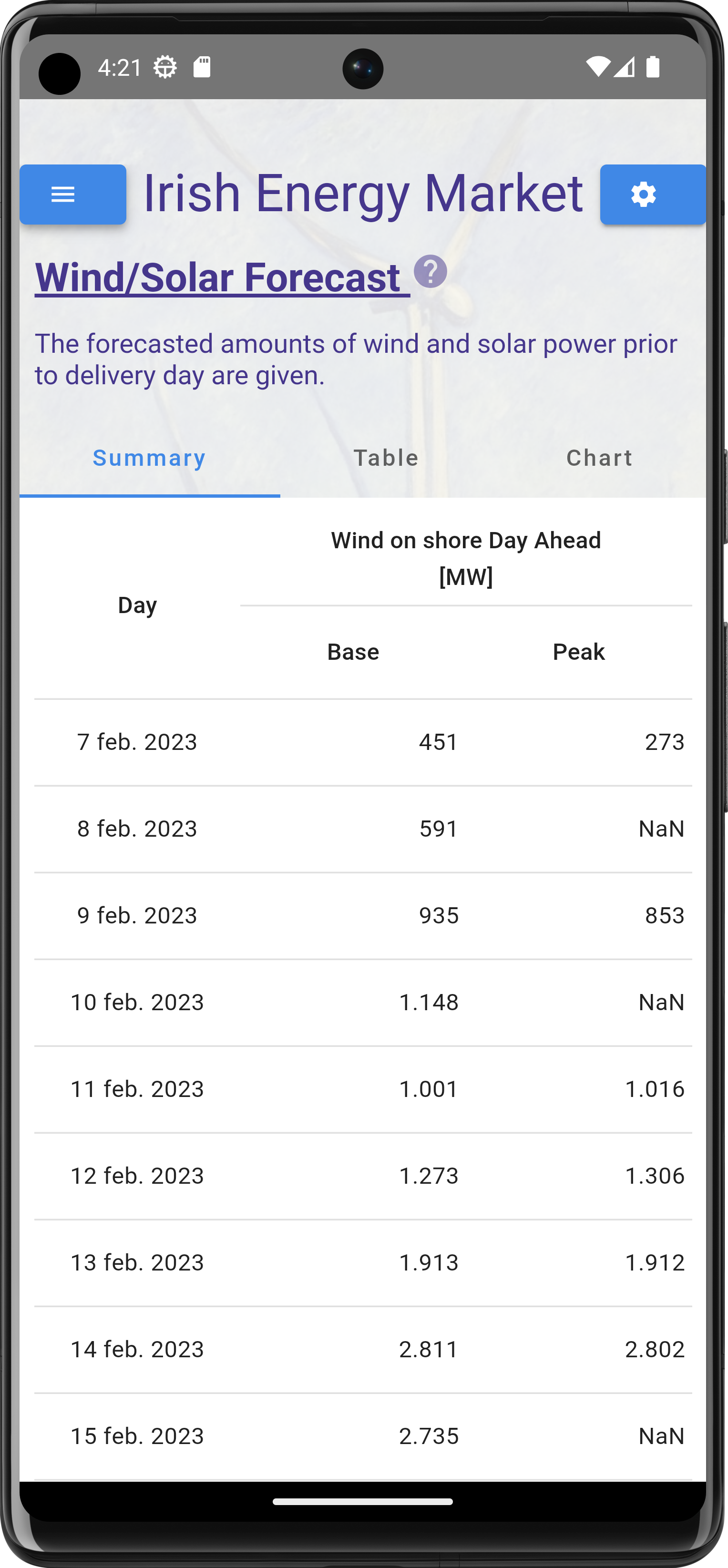
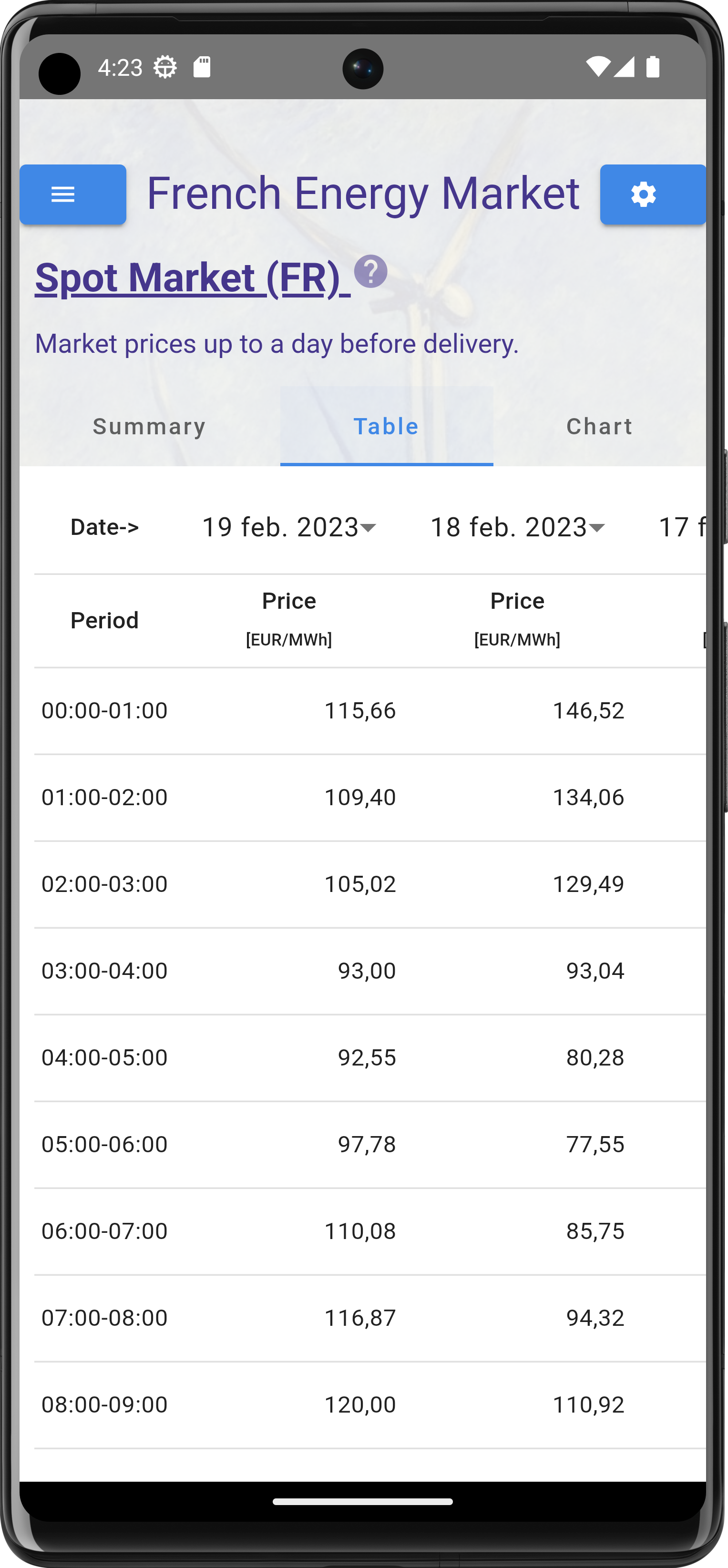
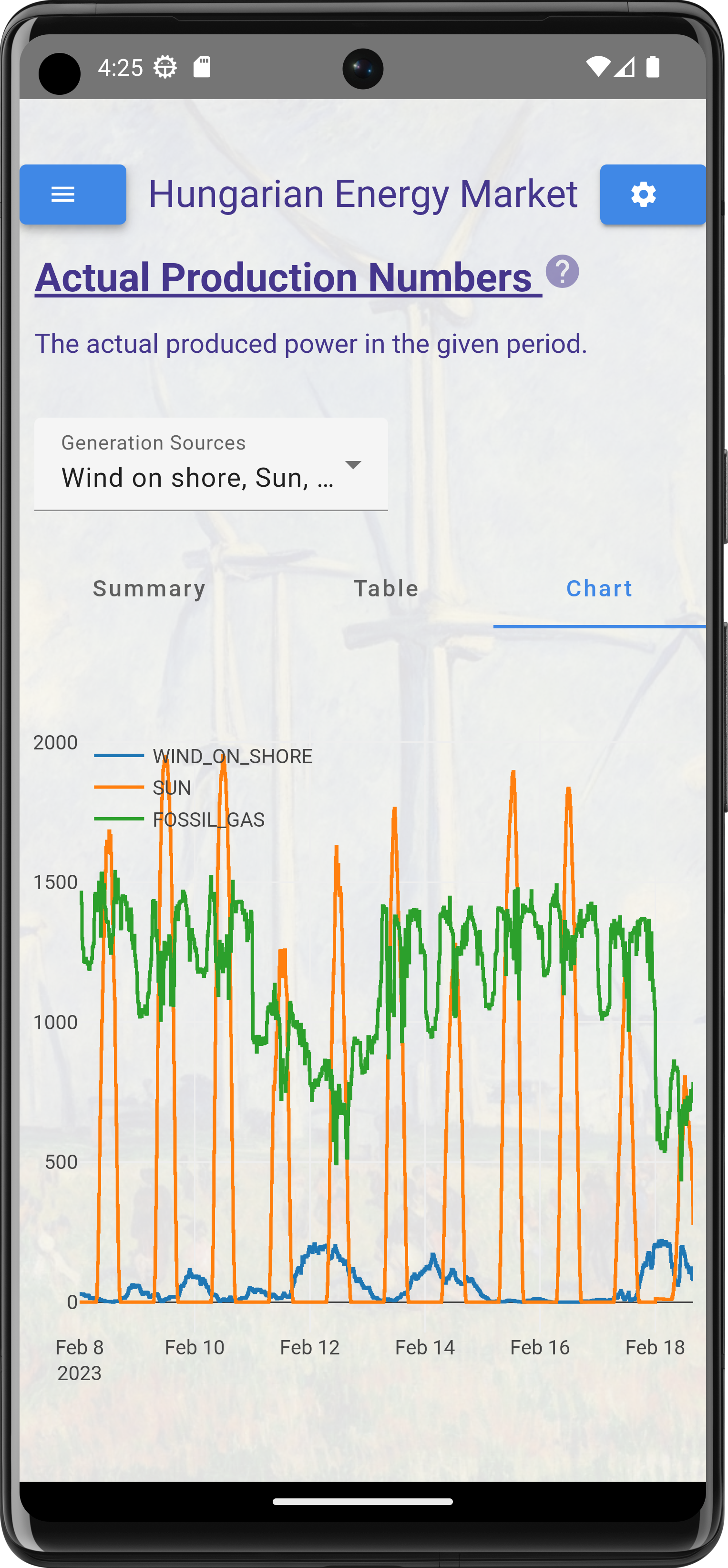
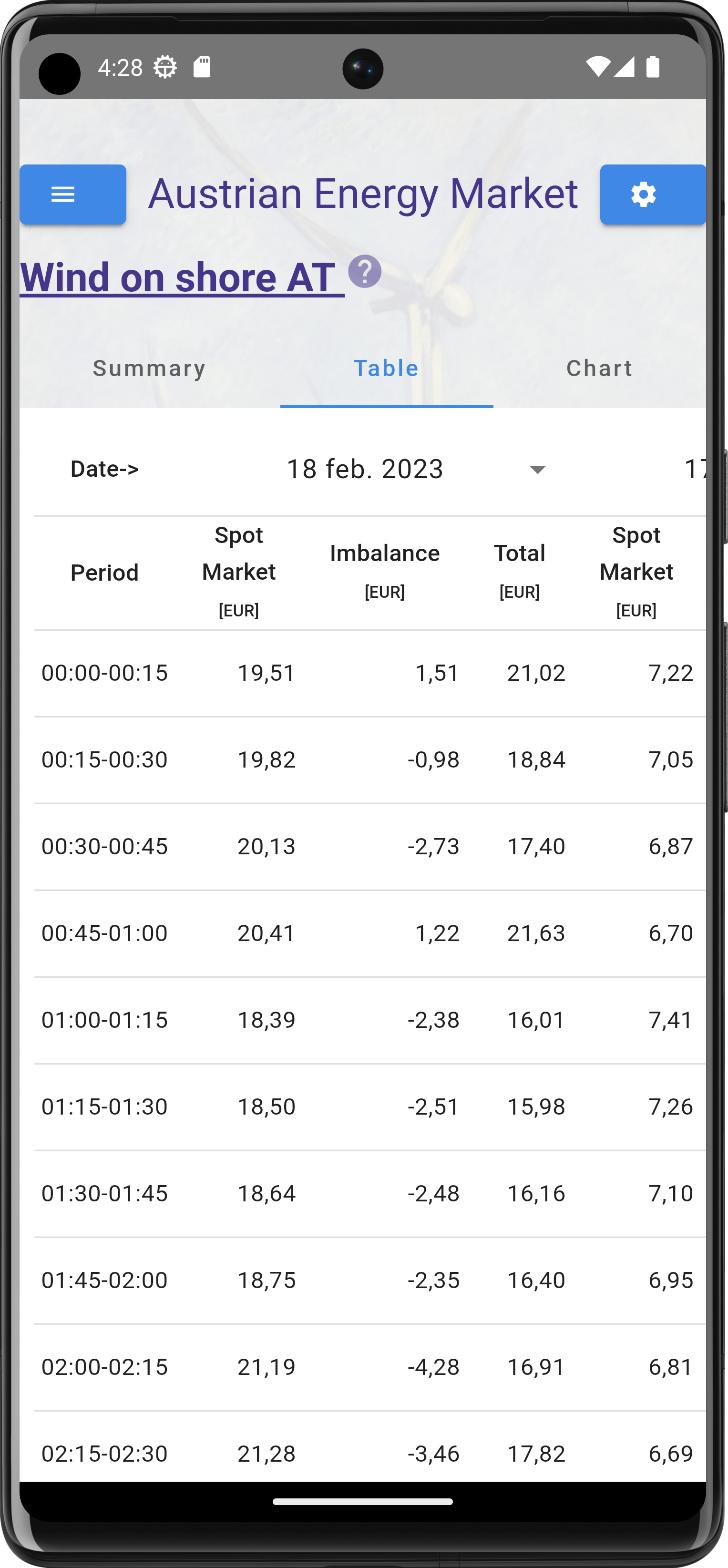
What price is used by the app
The app uses the resulting energy price from the (real time) energy balancing market. This is the final price paid by a producer/user for the difference between the forecasted energy production/consumption and the actual production/consumption. The price used is the price within the region where the installation is located.
How it works
TSOs are responsible for ensuring that the supply of electricity matches the demand at all times, as any deviation from this balance can cause disruptions to the grid. In order to achieve this, TSOs use the imbalance market to trade electricity with each other.
When there is a surplus of electricity in one country and a deficit in another, the TSOs can use the imbalance market to transfer electricity from the surplus country to the deficit country. This is done in real-time, based on the current demand and supply situation.
Benefits
The electricity imbalance market provides several benefits:
- It helps to ensure a stable and reliable electricity supply across Europe
- It facilitates the integration of renewable energy sources, which can be variable and unpredictable
- It promotes competition and reduces electricity prices for consumers
- It reduces the need for costly investments in generation capacity
Pricing in the Imbalance Market
Pricing is a critical aspect of how the electricity imbalance market in Europe operates. The prices for electricity in the imbalance market are typically set by the TSOs based on the supply and demand situation at any given moment.
The TSOs use a variety of different pricing mechanisms to set prices in the imbalance market, including:
- Balancing energy prices: These are prices that are set based on the cost of producing or consuming electricity at any given moment. They are typically used to incentivize market participants to either produce more electricity or reduce their consumption, depending on the supply and demand situation.
- Imbalance prices: These prices are set when there is a mismatch between the amount of electricity that is being produced and the amount that is being consumed. They are used to incentivize market participants to balance their production or consumption in order to avoid paying higher prices in the imbalance market.
- Cross-border balancing prices: These prices are set when TSOs need to exchange electricity with each other across national borders. They are typically based on the cost of transporting electricity between different countries.
In addition to these pricing mechanisms, there may also be other factors that can affect pricing in the imbalance market. For example, the availability of renewable energy sources such as wind and solar power can have an impact on pricing, as can weather conditions that affect electricity demand.
Challenges
Despite its benefits, the electricity imbalance market also faces several challenges:
- The market is still relatively new, and some countries have been slow to adopt it
- There are technical challenges associated with integrating the different national grids and ensuring that they can communicate effectively with each other
- There are also regulatory challenges associated with ensuring a level playing field for all participants in the market
Conclusion
The electricity imbalance market in Europe is an important mechanism for ensuring a stable and reliable electricity supply across national borders. While there are still some challenges to be addressed, the market has the potential to play a key role in the transition to a more sustainable, low-carbon energy system.